What are the secrets to success in responding to an FDA RTA Hold?
When an FDA reviewer places your 510k on RTA Hold, there are secrets you can learn to improve your chances of a successful response.
Test your knowledge about the FDA RTA Hold process
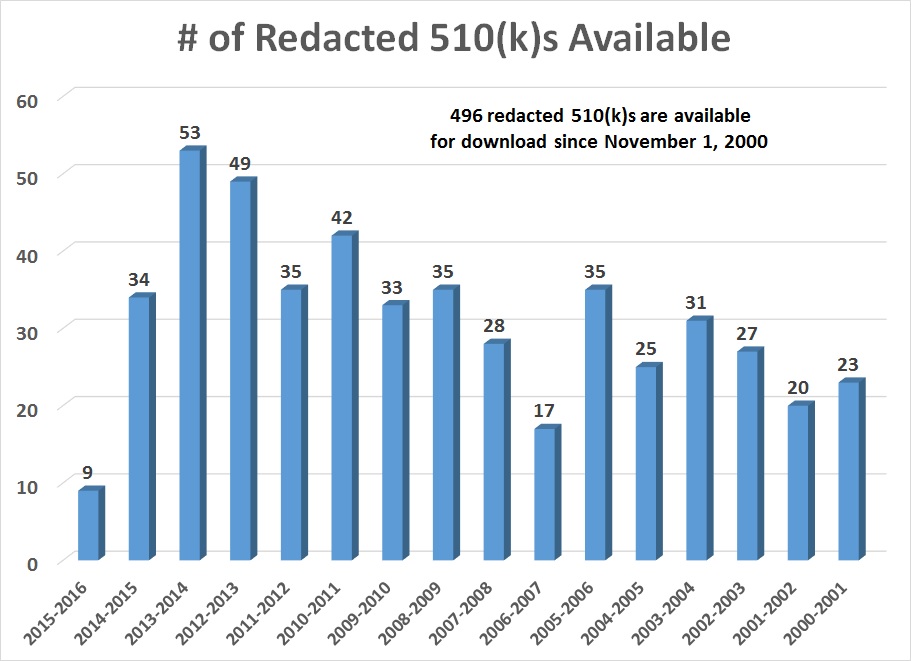
Did you know that approximately 50% of 510(k) submissions are placed on RTA Hold? Did you know that you can be placed on RTA Hold multiple times for the same submission? Did you know that the 90-day review clock is reset to “0” when you submit your response? Do you know how to respond to the FDA when the reviewer is incorrect? Did you know that you can avoid the RTA screening process for any 510(k) submission if you use the correct template? Every year there are more than 1,000 submissions placed on RTA Hold, but did you know there is an FDA guidance specifically telling you how to respond to deficiencies? You can learn the secrets to responding to an FDA RTA Hold just by reading this article.
What is an FDA RTA Hold?
When the FDA receives a Traditional 510k submission FDA eCopy, the eCopy is uploaded to the FDA system within hours of the submission being received. If the eCopy does not meet the eCopy format requirements, then the submission will be placed upon eCopy Hold. The official correspondent will receive an automated email indicating that the submission is on eCopy Hold, and the submitter will be asked to correct the submission format to meet the eCopy submission requirements and provide a replacement eCopy. If the FDA user fee has not cleared, then the submission will be placed on User Fee Hold. It is possible to be placed on eCopy Hold and User Fee Hold at the same time.
If your eCopy is accepted, then a reviewer is assigned to screen your submission for compliance with the FDA Refusal to Accept (RTA) policy. The reviewer has 14 days to complete this review, and on the 15th day the reviewer must do one of three things: 1) issue a RTA Hold letter to the submitter, 2) issue an RTA Acceptance letter to the submitter, or 3) issue a letter that states the RTA screening was not completed on-time and the submission was automatically accepted. If your receive an RTA Hold letter, it will be via email from the reviewer and the RTA Checklist will be attached. In the checklist, there will some items highlighted in yellow and deficiencies will be noted in those sections. The reviewer may add additional comments to the checklist, but you are only required to respond to the highlighted sections. The process that the reviewer follows for RTA screening is defined in the FDA guidance for the Refusal to Accept process, and the guidance includes a checklist for traditional, abbreviated, and special 510k submissions. Some companies will fill in these checklists themselves and submit a copy of the checklist with the 510k submission. This is intended to help the reviewer identify where all of the requirements in the RTA checklist can be found. Third-party reviewers require that the company complete the RTA checklist and provide it to them with the eCopy.
How many times can you be placed on hold for the same submission?
Technically there is no limit to the number of times a submission can be placed on RTA Hold, and our firm has seen a few submissions placed on RTA Hold twice in a row. The first RTA Hold is referred to as RTA1, and the response to that RTA Hold is referred to as the first supplement (i.e. K123456/S001). If a second RTA Hold is issued, that hold is RTA2, and the response to that RTA Hold is referred to as the second supplement (i.e. K123456/S002). A response to an eCopy Hold is referred to as an amendment (i.e. K123456/A001).
What happens to the 90-day review clock when you are placed on RTA Hold?
When the FDA reviewer places your submission on RTA Hold, the 90-day review clock is automatically reset. Therefore, even if you respond to an RTA Hold on the same day you receive the RTA Hold, and your submission is received the next day, the “real” review timeline is now 106 days instead of 90. If your submission is placed on RTA Hold twice, then the “real” review timeline is now 122 days instead of 90. If the lead reviewer of your 510k requests additional information, this is referred to as an “AI Request.” We will address this in a future blog, but an AI Request does not reset the review timeline. The AI Request, however, will increase the review timeline. Although we rarely have an RTA Hold, we almost always have an AI Request. This is why our average submission is approximately 125 days (i.e. ~30 days are required to respond to the AI Request.
How should you respond if the FDA reviewer is incorrect?
The average 510(k) submission has grown over time from 300 pages to more than 1,200 pages, but the FDA review “clock” is still 90 days and the RTA screening is limited to 15 days. Therefore, it is not reasonable for you to expect the reviewer to understand and absorb every detail of your submission. If the reviewer can’t find the information they are looking for quickly, the reviewer may state that they could not find the information in the submission or that you did not provide it. If the information is found in the submission, you should provide a reference to the section of the submission, including the document and page number, in your RTA response. You may even choose to quote the information in your response memo if it is brief.
Other times the reviewer may not understand why certain information is not relevant to your submission. In this case, you should restate why the information requested is not relevant. You may want to review relevant FDA guidance documents that explain how to justify why information is not required. For example, if you did not provide biocompatibility testing reports for some of the endpoints that are identified in ISO 10993-1:2018, then you should either provide a detailed biological risk assessment in accordance with the FDA guidance on the use of ISO 10993-1, or you should provide a biocompatibility certification statement.
If you are not sure why the FDA reviewer stated the information you provided is not acceptable, you might try calling or emailing the reviewer to ask for clarification. If you do this, be respectful of their time and be brief. You should identify who you are (you must be the official submission correspondent to speak with the reviewer), you should identify which submission you are contacting the reviewer about (they are working on many simultaneously), you should restate the issue identified by the reviewer (it may have been an issue of another member of the review team), and then you should indicate where the information can be found in the submission. If they believe this addresses the issue, then they will instruct you to provide that information in an RTA response. If the information does not address the issue, usually they will explain why. Your chances of receiving an email response are also better than speaking to the person on the phone–especially during the Covid-19 pandemic.
FDA eSTAR submissions are not subjected to the RTA screening process
When you use the FDA eSTAR submission instead of creating an eCopy, your submission should already meet all of the RTA screening requirements. The eSTAR includes automation to validate that the submission is administratively complete and therefore the reviewer does not need to do an RTA screening of an eSTAR submission. Therefore, most companies should realize a shorter overall 510k clearance timelines, because they will only have an AI Request and the review clock will not be reset.
Does the FDA offer any guidance on how to respond to deficiencies?
When the FDA writes deficiencies, the reviewer is supposed to follow the FDA guidance for deficiency content and format. However, the RTA checklist deficiencies typically are shorter and may not be as clear as a deficiency in additional information (AI) requests or non-substantial equivalence (NSE) letters. The first part of the deficiency is a reference to the information that was provided by the submitter (i.e. section, page number, or table). In an RTA checklist, each deficiency is provided in the comments section at the end of the section of the checklist. Therefore, if you have a deficiency related to your device description, the deficiency will be written at the end of the device description section of the RTA checklist. The comment will be highlighted in yellow, and there will be a checkbox next to the specific checklist item indicating that the requirement was not met. In the far-right column of the checklist, there will be a reference to the page of the submission where the deficiency can be found.
In the comment there reviewer should explain why the current information does not meet the requirement of the RTA checklist. The reviewer should also clarify the relevance of the deficiency with regard to the substantial equivalence determination. For the example of a deficiency related to your device description, usually, the issue is that your submission has inconsistencies between the various submissions or there is insufficient detail about your device. At the end of the comment, the reviewer should provide an explicit request for the information needed to address the RTA Hold.
In section “V” of the FDA guidance on deficiency responses, the FDA recommends that you restate the issue identified by the reviewer in your response. Next, your response should include one of the following:
- the information or data requested, or
- an explanation of why the issue is not relevant, or
- alternate information with an explanation of why the information you are providing addresses the issue.
Before you respond to an RTA Hold, you should look up any FDA guidance documents referenced in the RTA Checklist to make sure that you address each requirement in the applicable FDA guidance document(s).
The most important technique to learn when you are responding to regulators is to organize your response in a tabular format that is numbered in exactly the same order that the request was made. Typically there will also be sub-parts to certain issues. In that case, you should duplicate the numbers and/or letters of each sub-part and segregate each sub-part in a different row of the table. Personally, I like to alternate the color of the font I use in the table to make it even more obvious which information is a restatement of the reviewer’s comment and which information is the company’s response to the RTA Hold.
Regardless of how well your response is organized, you must respond within 180 days. On the 181st day, your submission will be automatically withdrawn. The agency has granted extensions of an additional 180 days during the Covid-19 pandemic, but that will end and you should verify if you can obtain an extension from the reviewer rather than assume that this will happen. If the 180th day is on a weekend or US holiday, the Document Control Center (DCC) at the FDA will not receive your submission until the next business day. Therefore, you will need to ship your submission earlier to ensure the delivery is received on time. Since most companies are shipping their RTA response via FedEx or UPS to the FDA, you also will want to make sure you take into account customs clearance for international shipments and local holidays where you are. If you are shipping from the UK, for example, you can’t expect FedEx to ship on a British holiday. If you need help with printing and shipping your RTA response, Medical Device Academy offers an eCopy print and ship service for $99/eCopy (including the overnight FedEx fee).
If your 510k submission was placed on RTA Hold by the FDA, we can help you respond to the deficiencies identified by the FDA reviewer. We can also review your planned response to identify potential gaps. If you need help please use our calendly app to schedule a call with a member of our team.
About the Author

Robert Packard is a regulatory consultant with 25+ years of experience in the medical device, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries. He is a graduate of UConn in Chemical Engineering. Robert was a senior manager at several medical device companies—including the President/CEO of a laparoscopic imaging company. His Quality Management System expertise covers all aspects of developing, training, implementing, and maintaining ISO 13485 and ISO 14971 certification. From 2009-2012, he was a lead auditor and instructor for one of the largest Notified Bodies. Robert’s specialty is regulatory submissions for high-risk medical devices, such as implants and drug/device combination products for CE marking applications, Canadian medical device applications, and 510(k) submissions. The most favorite part of his job is training others. He can be reached via phone 802.258.1881 or email. You can also follow him on Google+, LinkedIn or Twitter.
What are the secrets to success in responding to an FDA RTA Hold? Read More »




 Warning: If you are using Windows 10, and you save your eCopy or eSubmitter zip folder on a flash drive, Windows 10 will automatically create a hidden system folder titled “System Information Volume.” This folder is created as a security feature to enable you to recover accidentally deleted content. However, this folder results in an error when the FDA attempts to upload your submission automatically. Therefore, you must remove this hidden system folder. Instructions for this can be found on our website page about
Warning: If you are using Windows 10, and you save your eCopy or eSubmitter zip folder on a flash drive, Windows 10 will automatically create a hidden system folder titled “System Information Volume.” This folder is created as a security feature to enable you to recover accidentally deleted content. However, this folder results in an error when the FDA attempts to upload your submission automatically. Therefore, you must remove this hidden system folder. Instructions for this can be found on our website page about