How to implement a new ISO 13485 quality system plan in 2016
This article is a case study that explains how to implement a new ISO 13485 quality system plan at an accelerated schedule of just four months. The quality system will also be compliant with 21 CFR 820.
ISO 13485 quality system plan
Typically, I recommend implementing a new ISO 13485 quality system plan over a period of 6 months. The reason for this is that people can only read procedures and complete training at an individual pace. Since there are approximately 30 procedures required for a full-quality system, an implementation pace of one procedure per week allows a company to complete 90% of the reading and training in six months.
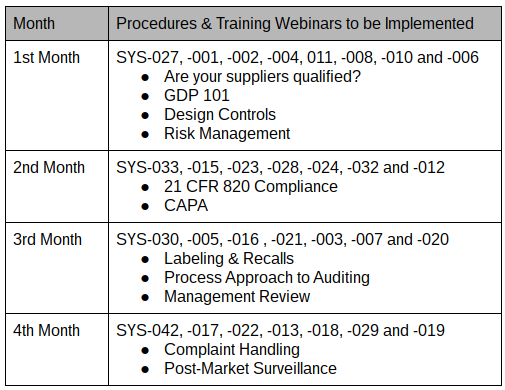
In October, a new client asked me for a proposal to implement a new ISO 13485 quality system plan. The proposed quality system plan indicated that the project would start in October and finish in March. The client accepted my proposal, but they asked me to help them implement the quality system plan in four months, as indicated in the table above. We just started the implementation of the quality system plan last week, and I have discovered some secrets that dramatically simplify the process. This blog shares some of the lessons learned that help implement the quality system plan at this faster pace.
Outsourcing ISO 13485 quality system development
Not everyone has the skill and experience to write a quality system procedure. Still, if you have a good template, you understand quality systems–then you can write quality system procedures. Depending upon the length of the procedure, it may take four to eight hours of writing for each procedure. Therefore, an in-house quality manager needs to allocate one day per week if they plan to write all the procedures for their quality system in six months. For a four-month implementation of an ISO 13485 quality system plan, you need to allocate two days per week to writing.
Alternatively, you can outsource the writing of your quality system. However, someone must be responsible for “customizing” generic procedures to fit your company, or the procedures need to be written from scratch. A third and final option is to have a hybrid of in-house procedures and outsourced procedures. If your quality manager has limited time resources, then you can supplement the managers’ time with procedures that are purchased and customized to fit your template. If there are specific procedures that the quality manager needs help with, such as risk management, then you can also purchase just those procedures.
Continuous Improvement
One of the basic principles of quality management systems is “continuous improvement.” The continuous improvement cycle is also known as the “Deming Cycle.” There are four parts to the cycle:
- Plan
- Do
- Check
- Act
When you are developing an ISO 13485 quality system, the first step is to develop the quality system plan. I recommend the following guidelines for a quality system plan. First, plan to implement the quality system at a steady pace. Second, organize the implementation into small groups of related procedures.
In this case study, I have 29 procedures that we are implementing, and there are 11 recorded training webinars. During each of the four months, approximately the same number of procedures are implemented. Then I organized the small groups of procedures around the scheduled webinar training. For example, the month of November will have a total of 24 documents (i.e., eight procedures and 16 associated forms and lists) implemented, and there are four webinar trainings scheduled. Therefore, four procedures related to “Good Documentation Practices 101“ will be implemented as a group under document change notice (DCN) 15-001. Two procedures associated with “Are your Suppliers Qualified? Prove it!“ will be implemented as a group under DCN 15-002. The remaining two procedures, design controls, and risk management, will be implemented as a group under DCN 15-003 with two related webinars on design controls and ISO 14971.
Document Change Notice (DCN)
The next step in the Deming Cycle is to “Do.” For the implementation of an ISO 13485 quality system plan, “doing” involves the creation of procedures, forms, and lists, but “doing” also involves the review and approval of these documents. The form we use to review and approve procedures is called a document change notice or DCN.
It’s been almost 20 years since I completed my first DCN. For anyone unfamiliar with the review and approval of new and revised documents, most quality systems document the review and approval of procedures and forms on a separate form. The reason for this is that when you make one change, it often affects several other documents and forms. Therefore, it is more efficient to list all the documents and forms that are affected by the change on one form. This results in fewer signatures for reviewers and approvers. Several of the companies that I have helped to implement an ISO 13485 quality system plan for failure to review and approve the documents and forms in a timely manner. I think there are two reasons for this:
- they haven’t been responsible for document control before, and
- they don’t want to have to create and maintain quality system records any sooner than required.
The first reason can be addressed quickly with training. The second reason, however, is flawed. It is essential to implement the procedures as soon as possible to begin creating quality system records that can be audited by an ISO 13485 certification auditor or by FDA inspectors for compliance with 21 CFR 820. I have struggled with this hesitation in the past, but for this project, I am completing DCNs for the initial release of all the procedures and forms. This ensures that all the procedures and forms will be reviewed and approved shortly after the webinar training is completed. Also, this gives my client multiple examples of DCNs to follow as they make revisions to the procedures and forms over time.
Quality Objectives & Data Analysis
The third step in the Deming Cycle is to “check.” I recommend using quantitative metrics to track progress toward your goal of completing the quality system implementation. For example, if you have 50 documents to review and approve, you can track the % complete by just multiplying each document that is approved by 2%. You can also track the implementation of documents separately by type. Every DCN you route for approval will take a certain number of days to complete. You might consider tracking the duration of DCN approval. As a benchmark, an efficient paper-based DCN process should average about four days from initiation to completion. I have seen average durations measured in months, but hopefully, your average duration of DCN approval will be measured in days. Another metric to consider is the % of required training that has been completed for the company, for each department, and for each employee. Regardless of which metrics you choose to evaluate your quality system implementation, you should pick some of these metrics as quality objectives (i.e., a requirement of ISO 13485, Clause 5.4.1). You should also analyze this data for positive and negative trends as required by ISO 13485, Clause 8.4.
Your first CAPAs
The fourth and final step in the Deming Cycle is to “act.” Acting involves taking corrective action(s) when your data analysis identifies processes that are not functioning as well as they should be. To achieve ISO 13485 certification, you will need some examples of corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs) that you have implemented. The steps you take in response to observed trends during data analysis are all potential CAPAs.
Download an ISO 13485 quality system plan
Later this week, I will be posting a follow-up blog that explains how to write an ISO 13485 quality system plan for establishing a new quality system. There will also be a link for downloading a free ISO 13485 quality system plan.
How to implement a new ISO 13485 quality system plan in 2016 Read More »