The FDA patches the regulations with guidance documents, but there is a desperate need to modernize 21 CFR 820 to ISO 13485.
FDA Proposed Amendment to 21 CFR 820
On February 23, 2022, the FDA published a proposed rule for medical device quality system regulation amendments. The FDA planned to implement amended regulations within 12 months, but the consensus of the device industry is that a transition of several years would be necessary. In the proposed rule, the FDA justifies the need for amended regulations based on the “redundancy of effort to comply with two substantially similar requirements,” creating inefficiencies. In public presentations, the FDA’s supporting arguments for the proposed quality system rule change rely heavily upon comparing similarities between 21 CFR 820 and ISO 13485. However, the comparison table provided is quite vague (see the table from page 2 of the FDA’s presentation reproduced below). The FDA also provided estimates of projected cost savings resulting from the proposed rule. What is completely absent from the discussion of the proposed rule is any mention of the need to modernize 21 CFR 820.
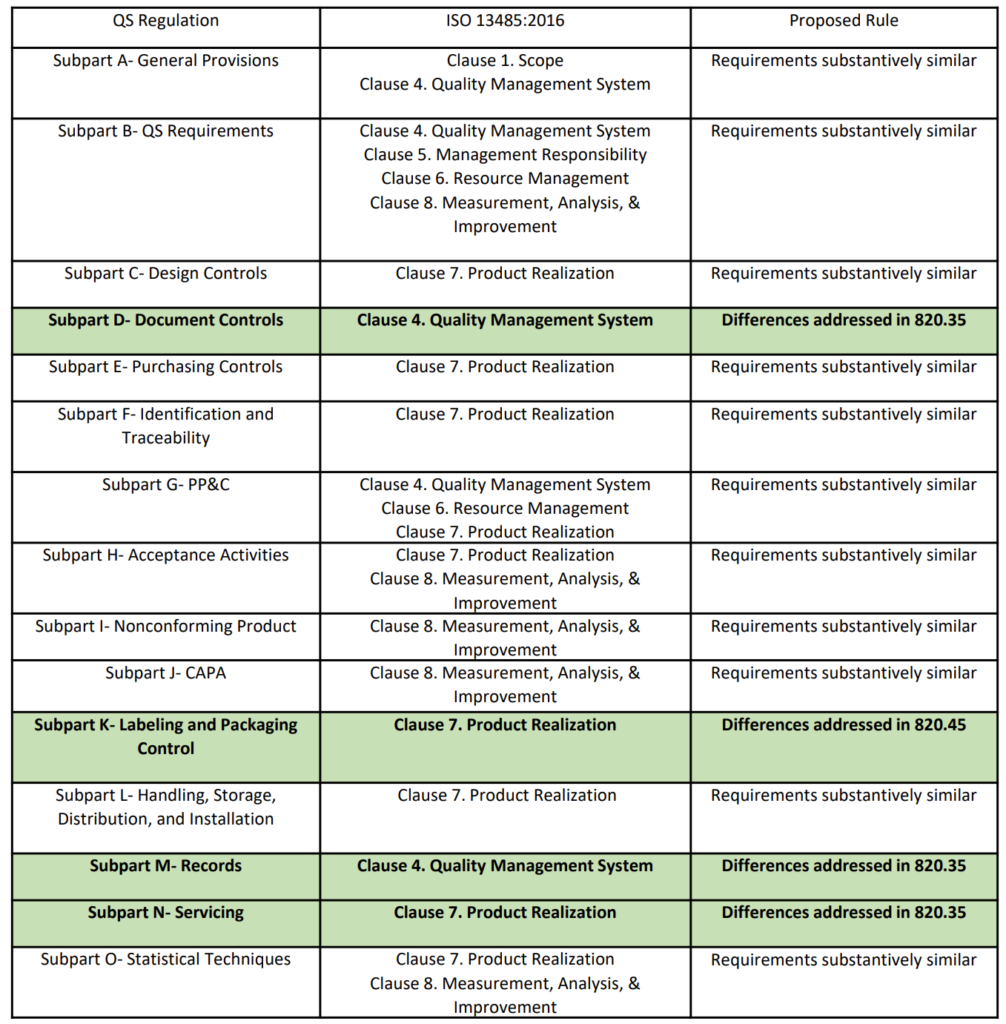
Are the requirements “substantively similar”?
The above table provided by the FDA claims that the requirements of 21 CFR 820 are substantively similar to the requirements of ISO 13485. However, there are some aspects of ISO 13485 that will modernize 21 CFR 820. The areas of impact are 1) software, 2) risk management, 3) human factors or usability engineering, and 4) post-market surveillance. The paragraphs below identify the applicable clauses of ISO 13485 where each of the four areas are covered.
Modernize 21 CFR 820 to include software and software security
Despite the limited proliferation of software in medical devices during the 1990s, 21 CFR 820 includes seven references to software. However, there are some Clauses of ISO 13485 that reference software that are not covered in the QSR. Modernizing 21 CFR 820 to reference ISO 13485 will incorporate these additional areas of applicability. Clause 4.1.6 includes a requirement for the validation of quality system software. Clause 7.6 includes a requirement for the validation of software used to manage calibrated devices used for monitoring and measurement. Clause 7.3 includes a requirement for validation of software embedded in devices, but that requirement was already included in 21 CFR 820.30. The FDA can modernize 21 CFR 820 further by defining Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), referencing IEC 62304 for management of the software development lifecycle, referencing IEC/TR 80002-1 for hazard analysis of software, referencing AAMI TIR57 for cybersecurity, and referencing ISO 27001 for network security. Currently, the FDA strategy is to implement guidance documents for cybersecurity and software validation requirements, but ISO 13485 only references IEC 62304. The only aspect of 21 CFR 820 that appears to be adequate with regard to software is the validation of software used for automation in 21 CFR 820.75. This requirement is similar to Clause 7.5.6 (i.e., validation of processes for production and service provisions).
Does 21 CFR 820 adequately cover risk management?
The FDA already recognizes ISO 14971:2019 as the standard for the risk management of medical devices. However, the risk is only mentioned once in 21 CFR 820. In order to modernize 21 CFR 820, it will be necessary for the FDA to identify how risk should be integrated throughout the quality system requirements. The FDA recently conducted two webinars related to the risk management of medical devices, but implementing a risk-based approach to quality systems is a struggle for companies that already have ISO 13485 certification. Therefore, a guidance document with examples of how to implement a risk-based approach to quality system implementation would be very helpful to the medical device industry.
Modernize 21 CFR 820 to include Human Factors and Usability Engineering
ISO 13485 references IEC 62366-1 as the applicable standard for usability engineering requirements, but there is no similar requirement found in 21 CFR 820. Therefore, human factors are an area where 21 CFR 820 needs to be modernized. The FDA has released guidance documents for the human factors content to be included in a 510k pre-market notification, but the guidance was released in 2016 and the guidance does not reflect the FDA’s current thoughts on human factors/usability engineering best practices. The FDA recently released a draft guidance for the format and content of human factors testing in a pre-market 510k submission, but that document is not a final guidance document and there is no mention of human factors, usability engineering, or even use errors in 21 CFR 820. Device manufacturers should be creating work instructions for use-related risk analysis (URRA) and fault-tree analysis to estimate the risks associated with use errors as identified in the draft guidance. These work instructions will also need to be linked with the design and development process and the post-market surveillance process.
Modernize 21 CFR 820 to include Post-Market Surveillance
ISO/TR 20416:2020 is a new standard specific to post-market surveillance, but it is not recognized by the FDA. There is also no section of 21 CFR 820 that includes a post-market surveillance requirement. The FDA QSR focuses on reactive elements such as:
- 21 CFR 820.100 – CAPA
- 21 CFR 820.198 – Complaint Handling
- 21 CFR 803 – Medical Device Reporting
- 21 CFR 820.200 – Servicing
- 21 CFR 820.250 – Statistical Techniques
The FDA does occasionally require 522 Post-Market Surveillance Studies for devices that demonstrate risks that require post-market safety studies. In addition, most Class 3 devices are required to conduct post-approval studies (PAS). For Class 3 devices, the FDA requires the submitter to provide a plan for a post-market study. Once the study plan is accepted by the FDA, the manufacturer must report on the progress of the study. Upon completion of the study, most manufacturers are not required to continue PMS.
How will the FDA enforce compliance with ISO 13485?
It is not clear how the FDA would enforce compliance with Clause 8.2.1 in ISO 13485 because there is no substantively equivalent requirement in the current 21 CFR 820 regulations. The QSR is 26 years old, and the regulation does not mention cybersecurity, human factors, or post-market surveillance. Risk is only mentioned once by the regulation, and software is only mentioned seven times. The FDA has “patched” the regulations through guidance documents, but there is a desperate need for new regulations that include critical elements. The transition of quality system requirements for the USA from 21 CFR 820 to ISO 13485:2016 will force regulators to establish policies for compliance with all of the quality system elements that are not in 21 CFR 820.
Companies that do not already have ISO 13485 certification should be proactive by 1) updating their quality system to comply with the ISO 13485 standard and 2) adopting the best practices outlined in the following related standards:
- AAMI/TIR57:2016 – Principles For Medical Device Security – Risk Management
- IEC 62366-1:2015 – Medical devices — Part 1: Application of usability engineering to medical devices
- ISO/TR 20416:2020 – Medical devices — Post-market surveillance for manufacturers
- ISO 14971:2019 – Medical Devices – Application Of Risk Management To Medical Devices
- IEC 62304:2015 – Medical Device Software – Software Life Cycle Processes
- ISO/TR 80002-1:2009 – Medical device software — Part 1: Guidance on the application of ISO 14971 to medical device software
- ISO/TR 80002-2:2017 – Medical device software — Part 2: Validation of software for medical device quality systems
What is the potential impact of the US FDA requiring software, risk management, cybersecurity, human factors, and post-market surveillance as part of a medical device company’s quality system?
