The article shares lessons learned from implementing procedures for a new ISO 13485 quality system. This is the second in a series. The first month of procedure implementation was covered in a previous article titled, “How to implement a new ISO 13485 quality system plan in 2016.”
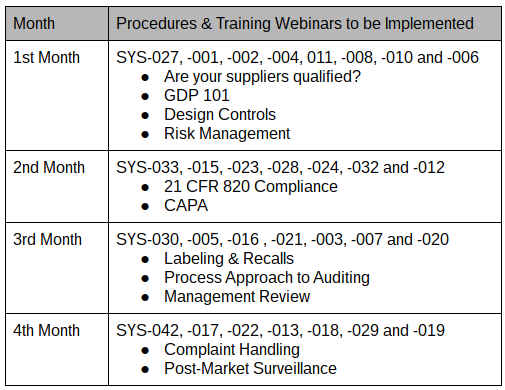
Typically, I recommend implementing a new ISO 13485 quality system over six months. Still, recently I a few clients have requested my assistance with implementing a quality management system within four months. In November, I wrote an article about implementing a new ISO 13485 quality system. That article described implementing procedures for the first month. Specifically, the implementation of the following procedures was covered:
- SYS-027, Purchasing
- SYS-001, Document Control
- SYS-002, Record & Data Control
- SYS-004, Training & Competency
- SYS-011, Supplier Quality Management
- SYS-008, Product Development
- SYS-010, Risk Management
- SYS-006, Change Control
These eight procedures are typically needed first. This article covers the implementation of the next set of procedures. During this month, I recommend conducting company-wide quality management system training for the ISO 13485 and 21 CFR 820.
Implementing Receiving Inspection Procedures
During the first month, procedures for purchasing components and services are implemented. As these products are shipped and received by your company, you need to create records of incoming inspection. It is not sufficient to merely have a log for receiving inspection. You need records of the results of the inspection. You may outsource the inspection activities, but receiving personnel must review the records of inspection for accuracy and completeness before moving product to your storage warehouse or production areas. Even if the inspection is 100% outsourced, it is still recommended to verify the inspection results independently on a sampling basis periodically. This should be a risk-based sampling that takes into account the importance of the item being inspected and the existence of in-process and final inspection activities that will identify potential nonconformities.
The most challenging part of this process typically is identifying inspection procedures and calibrated devices for inspection. Your company must find a balance between inspections performed by suppliers, incoming inspection, in-process inspection, and final inspection. Each of these process controls requires time and resources, but implementation should be risk-based and take into account the effectiveness of each inspection process–as determined by process validation. Sample sizes for inspection should also be risk-based.
Implementing Procedures for Identification and Traceability
The lot or a serial number of components must be identified throughout product realization–including incoming inspection, storage, production, final inspection, and shipping. In addition to determining what things are, you must also identify the status of each item throughout the product realization process. For example:
- Is the product to be inspected or already inspected?
- After the inspection, is product accepted or rejected?
- Which production processes have been completed?
- Is the product released for the final shipment?
The procedure for identification and traceability should be implemented immediately after the purchasing process, implemented during 1st month, because traceability requirements should be communicated to suppliers as part of supplier quality agreements and as part of each purchase order.
Initially, when this process is implemented, there is a tendency to complete forms for every step of the process and to distribute copies of the forms to communicate status. Completing forms and copying paperwork requires labor and adds no value. Therefore, learn manufacturing methods and visual indicators such as color-coding are recommended as best practices for identifying products and their status.
Implementing CAPA Procedures
When a product is identified as nonconforming, corrective actions need to be implemented to prevent a recurrence. Procedures need to include the requirement for planning corrective actions, containing a nonconforming product, correcting nonconformities, and implementing actions to prevent any future nonconformities. These procedures also need to address negative trends to prevent nonconformities before the product is out of specification (i.e., preventive actions). Procedures also need to provide guidelines on how to verify the effectiveness of corrective and preventive actions. Initially, the actions implemented will be specific to a purchased product that is received and rejected. However, over time data analysis of process monitoring and internal auditing will identify additional corrective and preventive actions that are needed.
The effectiveness of CAPA processes, in general, requires three key elements:
- A well-designed CAPA form
- Proper training on root cause analysis
- Performing effectiveness checks
In the CAPA training provided during the second month, the best practices for CAPA form design are covered. The training includes several methods for root causes analysis too. Finally, the training emphasizes using quantitative measurements to verify the effectiveness of corrective actions. It is recommended to identify the quantitative acceptance criteria for an effective corrective action before initiating actions to ensure that the actions planned are sufficient to prevent a recurrence.
Monitoring Your Procedure Implementation Process
As indicated in November’s article, I recommend using quantitative metrics to track the progress of procedure implementation. For example:
- % of procedures implemented,
- duration of document review and approval process, and
- % of required training completed.
Implementing Procedures for ISO 13485:2016
If you already have a quality system in place, you are implementing procedures that are modified for ISO 13485:2016 compliance, some of the same lessons learned to apply. If you are interested in learning more about the changes required for compliance with the 2016 version of the standard, we recorded two live webinars on March 24, 2016.

Pingback: Process Approach to Auditing - 7 Steps to Training Auditors - Medical Device Academy Medical Device Academy