This article describes how to perform IFU validation before commercialization and how to conduct post-market surveillance to ensure that your IFU continues to be suitable as your user population and patient population expand.
Most companies create an IFU for a new product by plagiarism. They merely copy a competitor’s IFU and change the name. If a regulatory expert creates the IFU, the IFU will be nearly identical to the competitor IFU. However, if a marketing person creates the IFU, the IFU will explain how your product is different from the competitor’s product. Neither approach is practical.
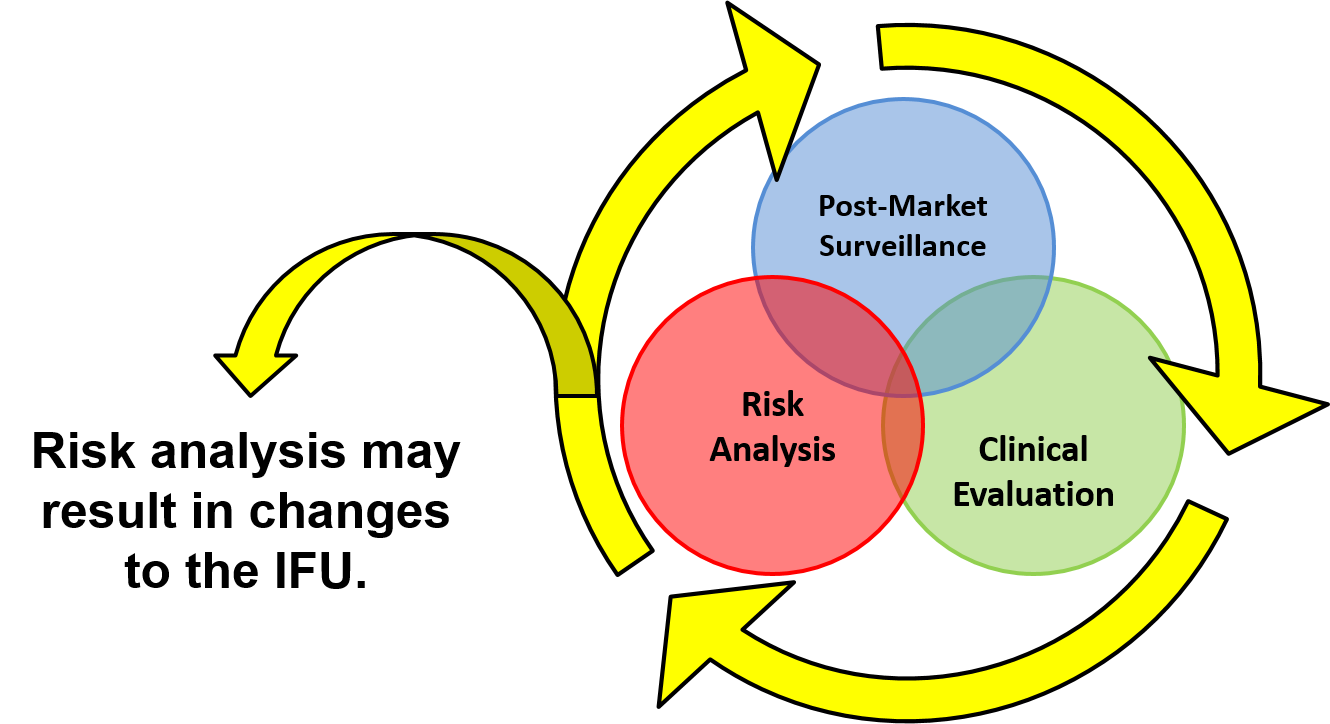
Creating a risk-based IFU
EN ISO 14971:2012 identifies deviations between the ISO 14971:2007 international standard and the three EU Directives. However, deviation #7 is specific to labeling and instructions for use. Even if your product is not CE marked, you should be developing a risk-based approach to IFUs. The priority of risk controls is to eliminate and reduce risks by design, manufacture, and selection of materials. The second priority is to implement protective measures such as alarms to warn users of risks. The last priority for risk controls is to inform users of residual risks. The best practice is to utilize a risk traceability matrix to document each of the risk controls you implemented to eliminate and reduce the risks of hazards identified.
The EN version of ISO 14971 will not allow you to reduce risks quantitatively in your risk assessment for information provided to users about risks, because this type of risk control is not entirely effective. However, you are required to verify that each residual risk is disclosed to users in your IFU, and you must validate that your warnings, precautions, and contraindications are adequately identified such that users understand the residual risks. You are also required to determine any user training needed to ensure specified performance and safe use of your medical device in accordance with ISO 13485:2016, Clause 7.2.1d. Clause 7.2.2d) requires that your company ensure that user training is made available. Any user training you provide should also be validated for effectiveness.
When to perform IFU validation
Some companies ask physicians that helped them with product development review draft IFUs. However, these physicians are already familiar with your product, and your company, and they are highly skilled in the specific procedures your device will be used for. After your experts have made their final edits to your draft IFU, you now need a “fresh set of eyes.” The best approach is to validate the effectiveness of your IFU with potential users that don’t know you or your company. If your product requires animal performance testing or human clinical studies, you could use these studies to validate your IFU. However, I recommend conducting a simulated use study before conducting animal or human studies. Conducting a simulated use study before animal and human studies can prevent deviations from your documented protocols that were caused by the inadequate review of the IFUs.
Methods of IFU validation
The best method for validating your IFU is to perform a simulated use study or human factors study. The FDA published a human factors guidance document that can help you assess the risk of human factors and ergonomics. The FDA guidance requires that you identify your intended user population(s). For each individual population of users, you are required to have a minimum of 15 users for your study. If your product is not for specific indications, you may be able to select 15 users at a few sites randomly. However, if your device is intended for two different specialties, then you need 30 users–15 for each specialization. I recommend recording a video of simulated use studies too. Videos identify small details that you might miss, and clips from the videos are useful in creating training videos for future users.
Gathering Post-Market Surveillance
Post-market surveillance is not just asking customers if they are satisfied. You need to continue to monitor adverse event databases, your complaint database, and any service records to determine if there are any new risks and to verify that the risks you identified were accurately estimated concerning severity and probability of occurrence of harm. Clinical studies and PMS are the only way you can gather data regarding the likelihood of occurrence of harm. When you design your post-market surveillance questions, make sure you include questions explicitly targeting the residual risks you identify in your IFU. You should also ask, “What indications do you use this device for. Specifically, please identify the intended diagnosis, treatment, and patient populations.” This wording is more effective than asking if a physician is using your product “off label.”
Revalidation of IFU after labeling changes
Changes to labeling and IFUs should always be considered design changes and may require revalidation. If the switch is in response to a complaint or CAPA, then you must revalidate the IFU and labeling to verify the effectiveness of your corrective action. Any validation should be documented, reviewed, and approved before implementation, and acceptance criteria should be determined ahead of time. Your acceptance criteria should be quantitative, so you can objectively determine if the change is valid or not. You might be able to copy your previous IFU validation protocol or simulated use protocol and simply repeat the validation precisely as you did before with new users. However, sometimes the reason why the IFU was not 100% effective in the past is that the risk you are addressing in the revised IFU was not evaluated adequately in the original simulated use protocol.
New webinar for risk-based IFU validation and PMS
If you want to learn more about using a risk-based approach to developing IFUs, validating IFUs, and performing post-market surveillance to monitor the effectiveness of your IFU, then please click on the webinar link below.
If you are interested in ISO 14971 training, we were conducting a risk management training webinar on October 19, 2018.


Pingback: ISO 14971 - Medical Device Academy Risk Management Updates Medical Device Academy